Understanding OWIN and Katana Middleware Components
In this tutorial , I will talk about owin and katana.
Owin means Open Web Interface for .NET and defines a standard interface between .NET web servers and web applications (www.owin.org) . KATANA is microsoft implementation of OWIN Specification.
OWIN is just a specification that abstract the way we build web applications without taking care of how they will be hosted.
So we will focus only on solving the problem so as to build very flexible web applications.
Middleware components are pieces of code added to our application pipeline and whose job is to handle each request and response.
To follow this tutorial, you must undertand ASP.NET and Asynchronous Programming with async and await
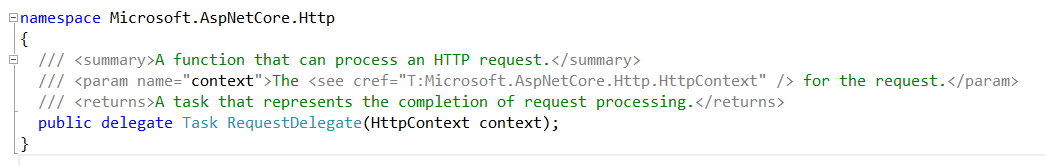
In ASP.NET core we achieve this goal by using a RequestDelegate :
But using Asp.NET MVC5, we can define a RequestDelegate by using a delegate and a dictionary from a Func

![]()
It use a dictionary that contains all informations in the HttpRequest send to the server , and a Task that process the request
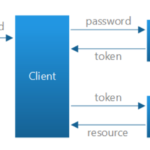
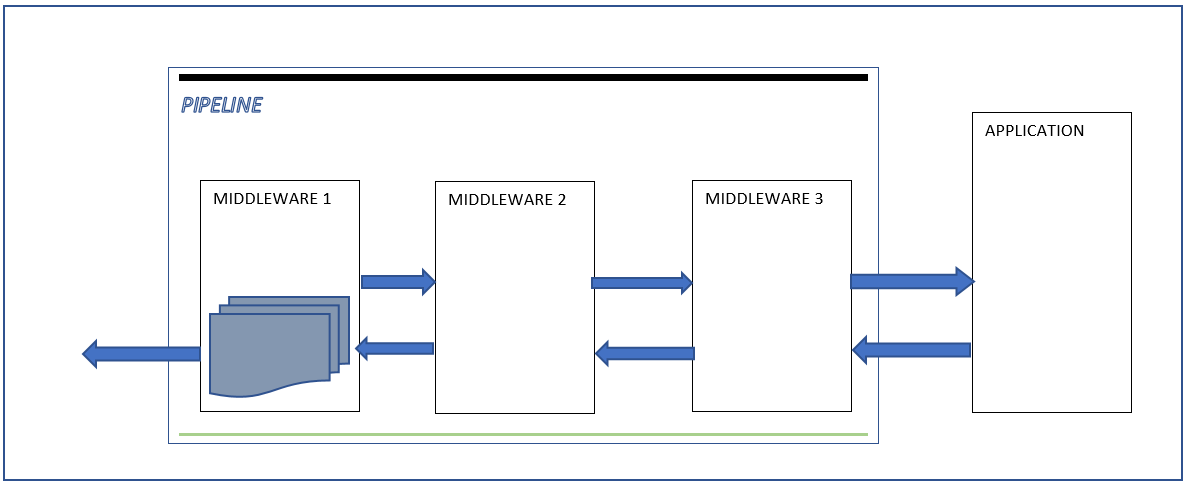
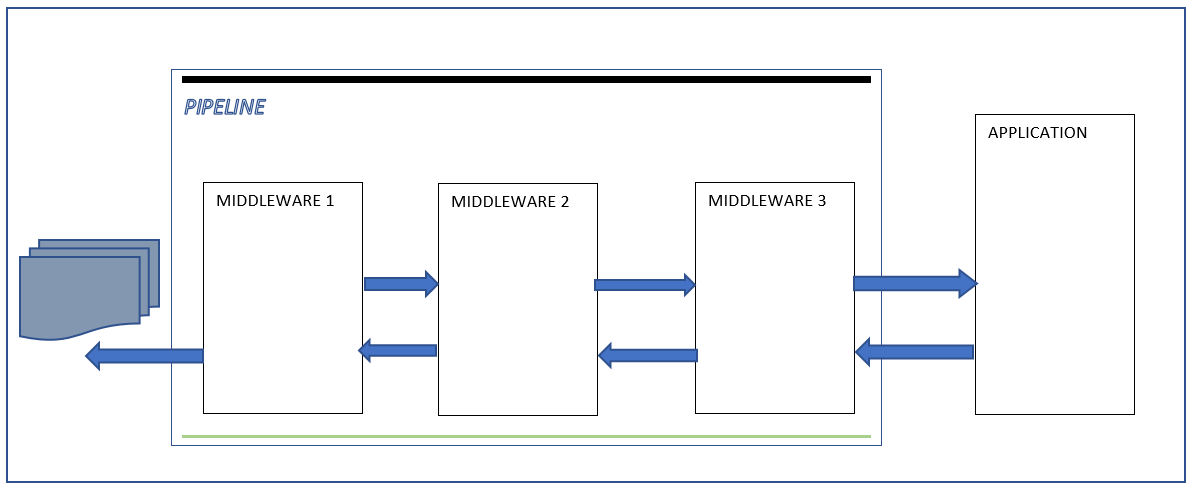
HOST : Console application, windows service or IIS, etc…
SERVER : Receive incoming HttpRequest and send HttpResponse
MIDDLEWARE : is similar to HttpModule but not depend on IIS
APPLICATION : Generate the response
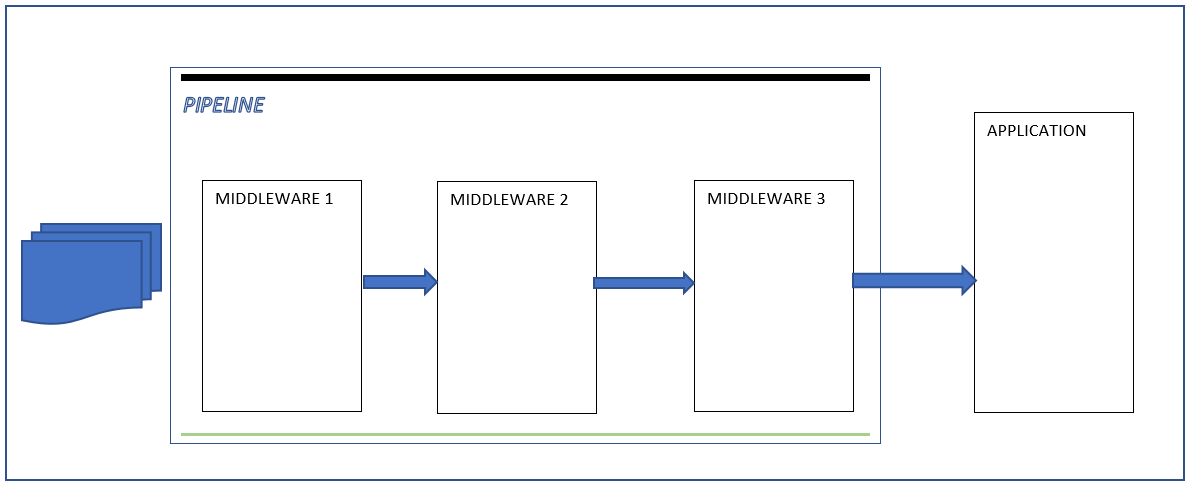
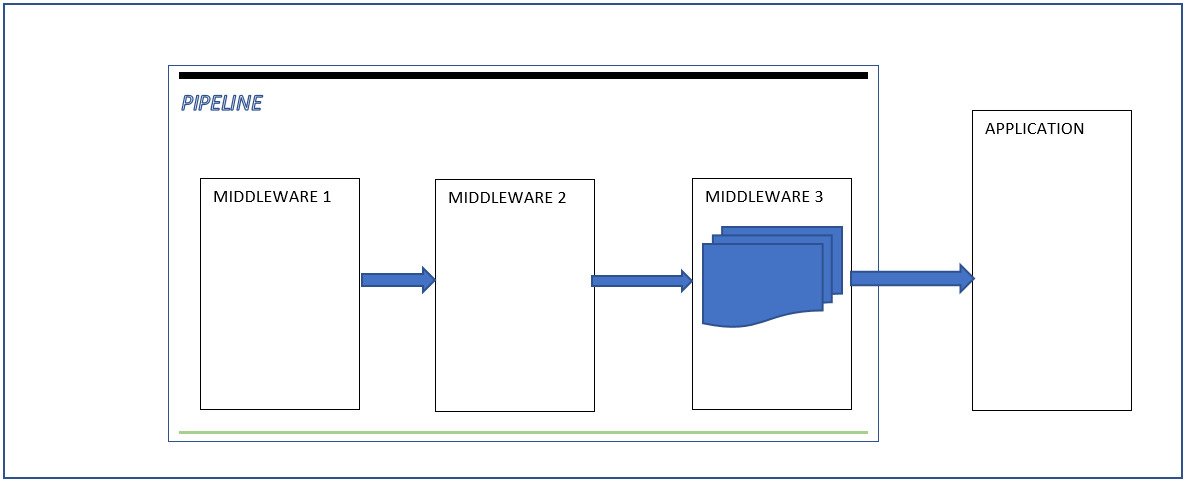
So client connect to the server and send HttpRequest, then the server split request into an environment dictionary ( Method , Path ,RequestBody,ResponseBody).
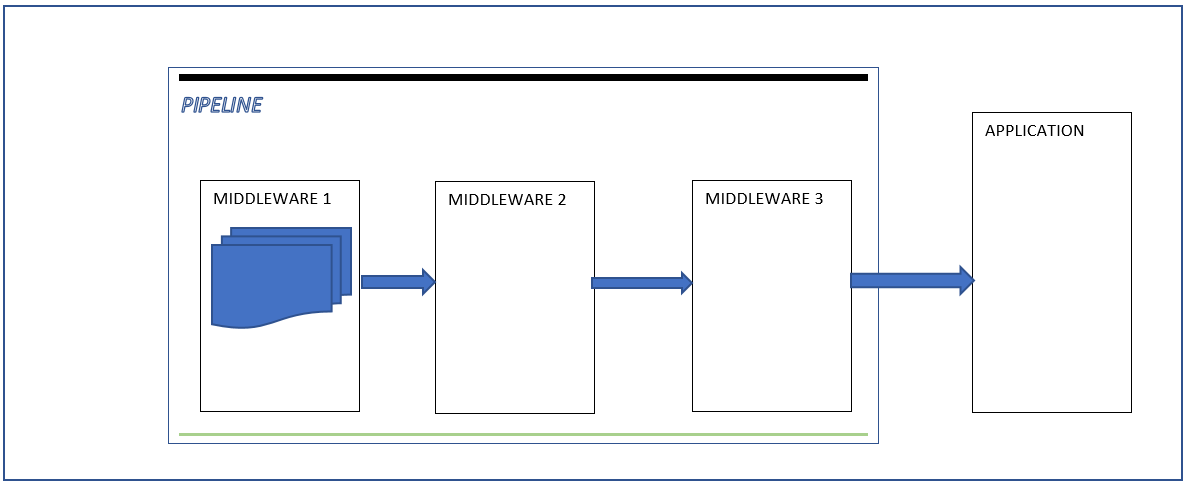
The server pass the environment dictionary to the first Middleware of the pipeline using the RequestDelegate and return a Task
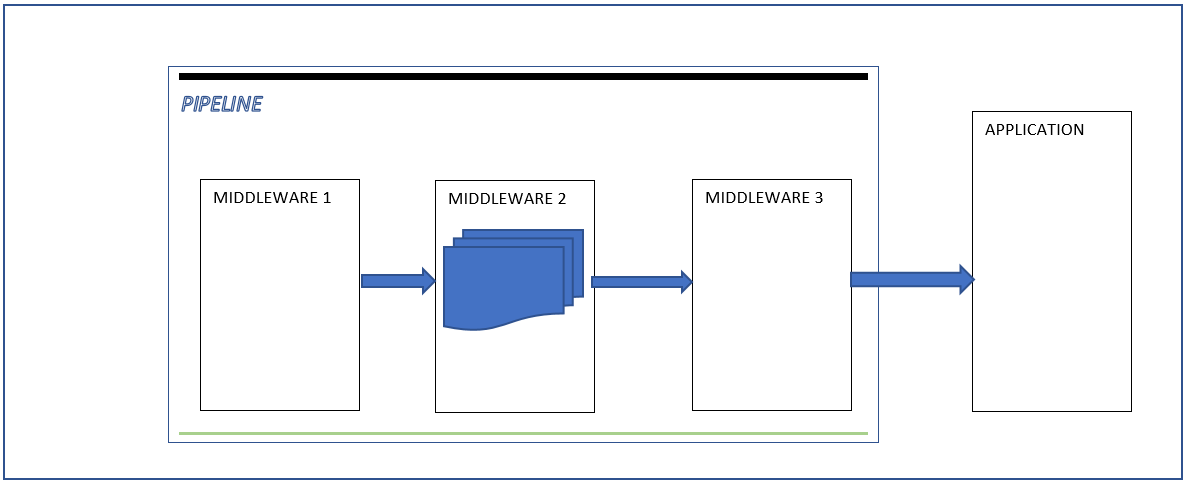
The first Middleware process the request according to information in the dictionary and then pass the dictionary to the next Middleware,
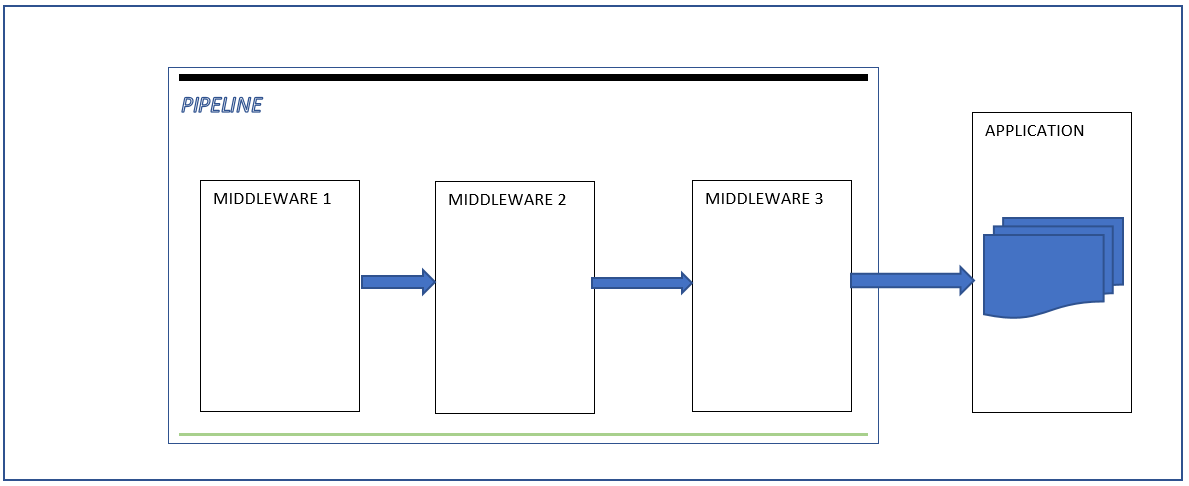
The process continues until the application , then the application generate the response and send it back to the last Middleware.
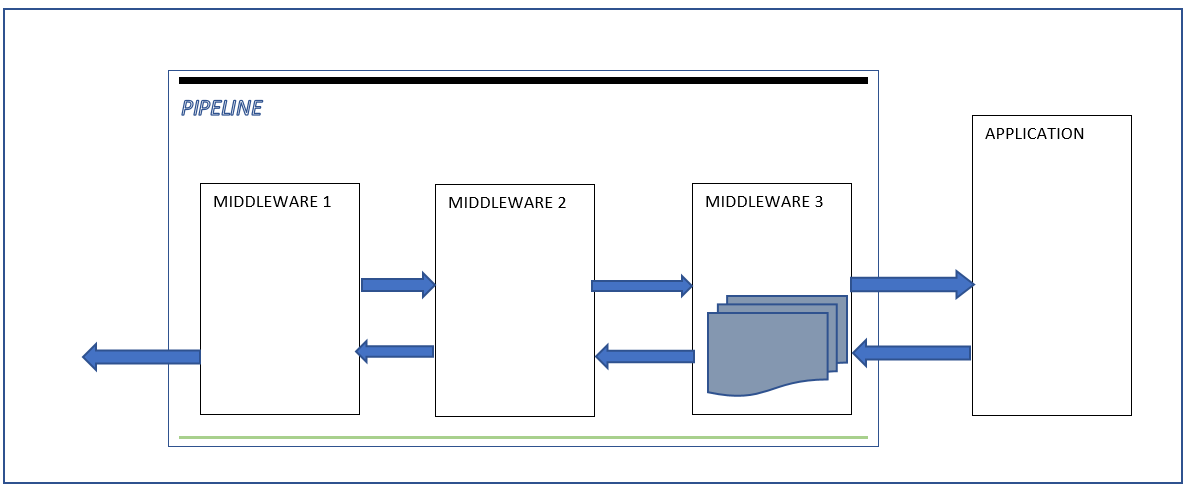
The last Middleware process the request according to information in the dictionary and then pass the dictionary to the previous Middleware in the pipeline
If the dictionary reaches the beginning of the pipeline, the server notify the completion of the processing by the task returing from the RequestDelegate and finally the server send response to the client
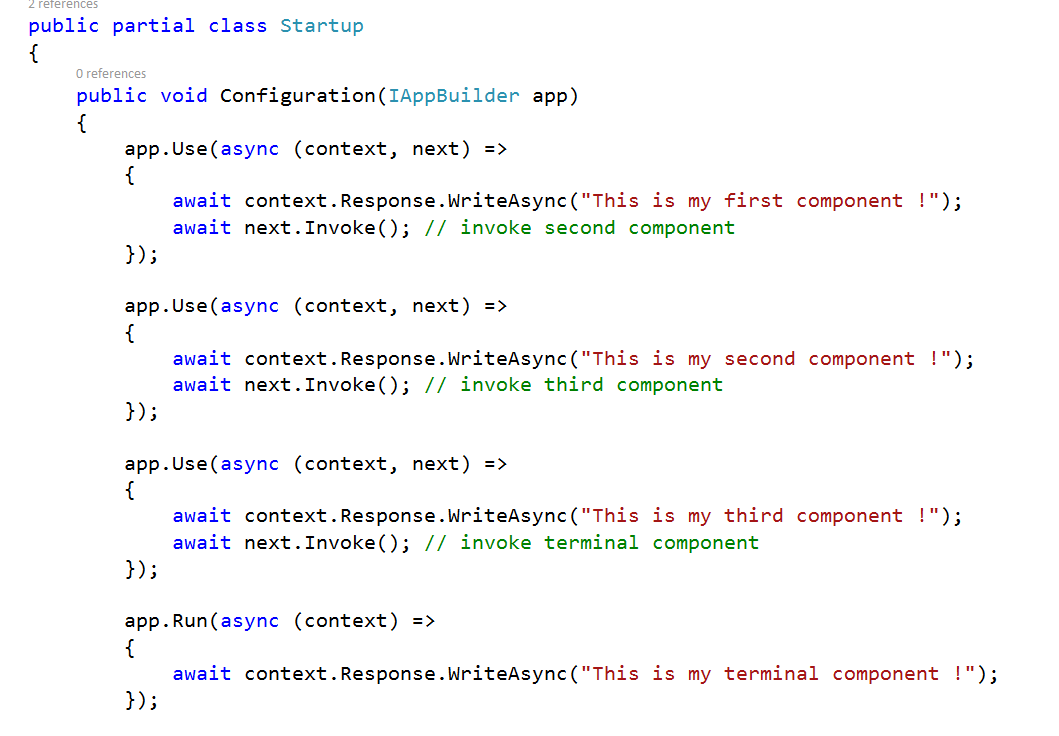
Creating our first middleware Components
Create an asp.net MVC5 application or ASP.NET core application
locate the Startup class and add the following :
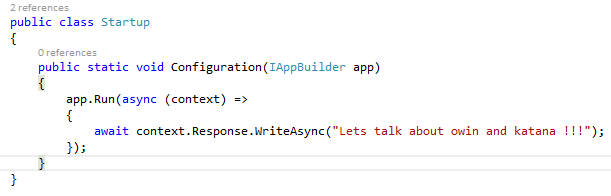
app.Run(async (context) =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync(“Lets talk about owin and katana !!!” );
});
This is our first component . it uses a Run method wich accept a RequestDelegate and returns a Task
public delegate Task RequestDelegate(HttpContext context);
This middleware component handles each request and create a response.
Run is a method that use a RequestDelegate wich is terminal to the pipeline and should only run at the end of the pipeline
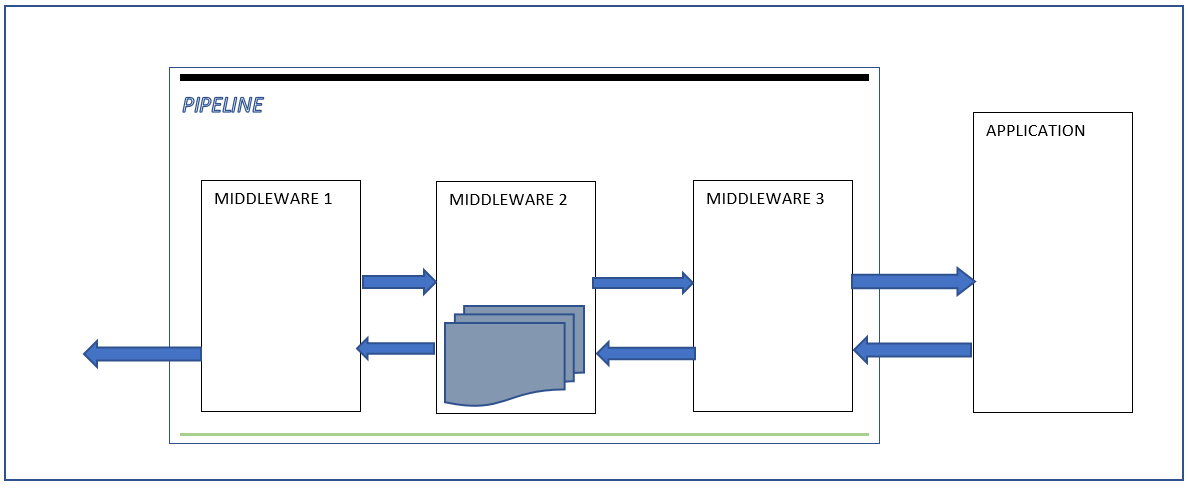
So to control the order in wich middleware components are added in the application pipeline
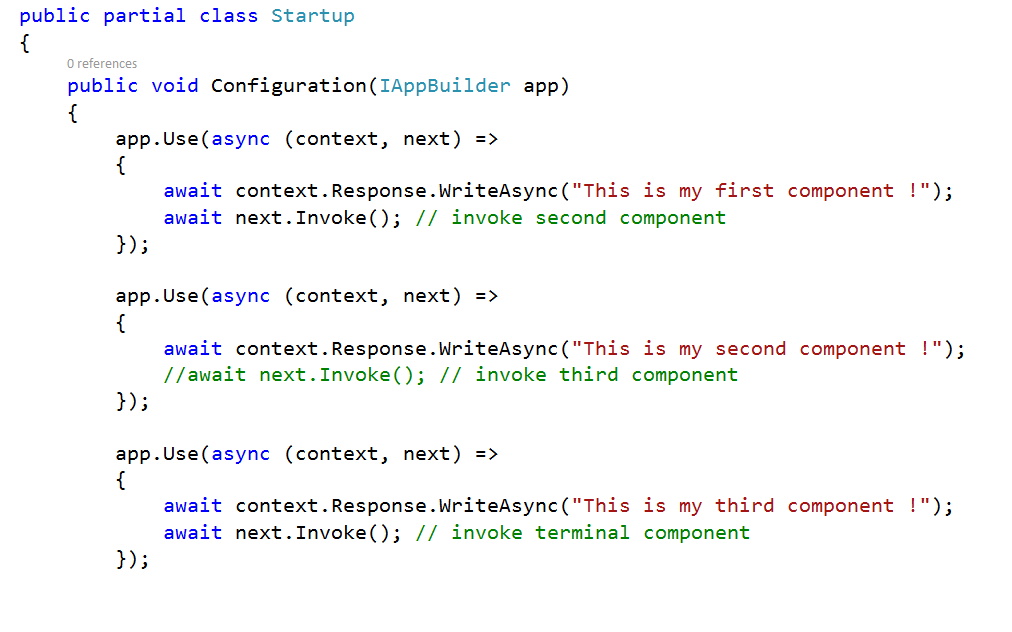
by missing await next.Invoke(); the current middleware will be executed and terminate the pipeline
So in the figure below my second component will run and terminate the pipeline because await next.Invoke(); is commented in my second component
Map
Map ( string pathMatch, Action<IAppBuilder> configuration)
If the request path starts with the given path (MyBranchOne) executes the following code instead of continuing to the next component in the pipeline
Example : http://localhost:5643/MyBranchOne)
 It is also possible to execute the following middleware before returning back and executing the rest of the current branch
It is also possible to execute the following middleware before returning back and executing the rest of the current branch

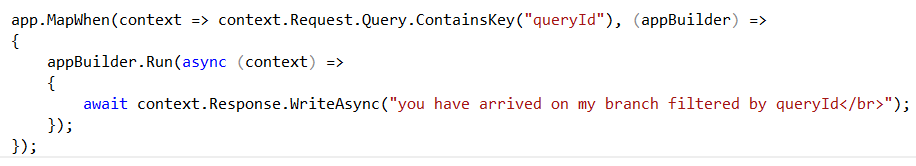
MapWhen
MapWhen(this IAppBuilder app, Func<IOwinContext, bool> predicate, Action<IAppBuilder> configuration);
Branches the request pipeline based on the QueryString
Example : http://localhost:5643/?queryId=test
Executes if QueryString contains queryId
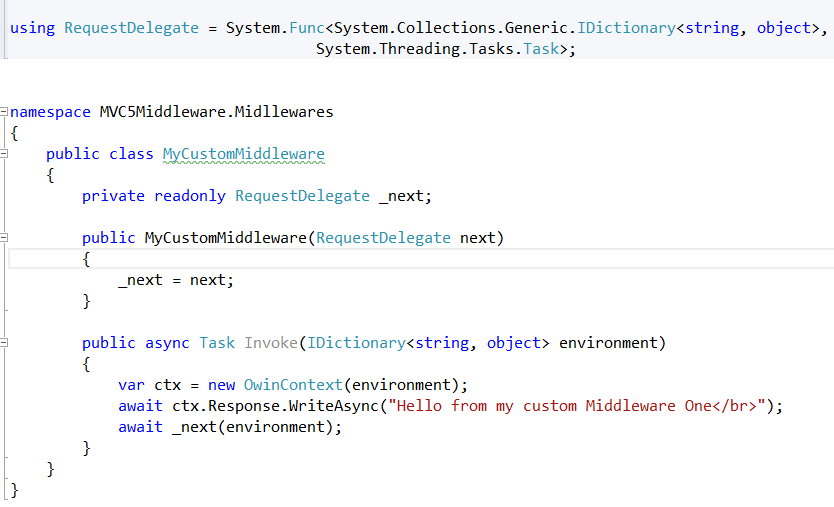
Creating a Custom Middleware
To create our custom middleware we are going to define a RequestDelegate wich is an AppFunc that takes a dictionary<string,object> and returns a Task
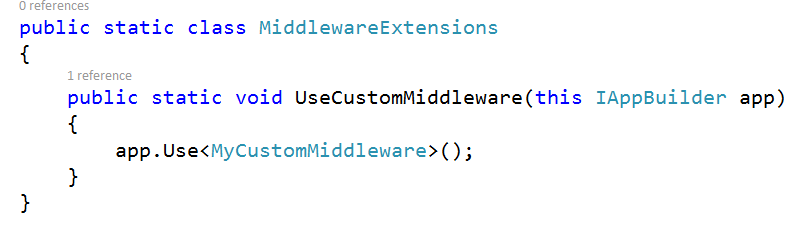
To include our custom middleware in the application pipeline, we must define an extension method like this
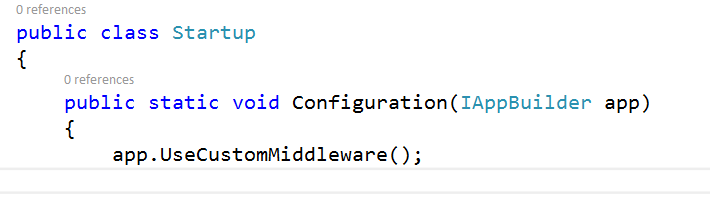
And finnaly use our extension method in Startup class
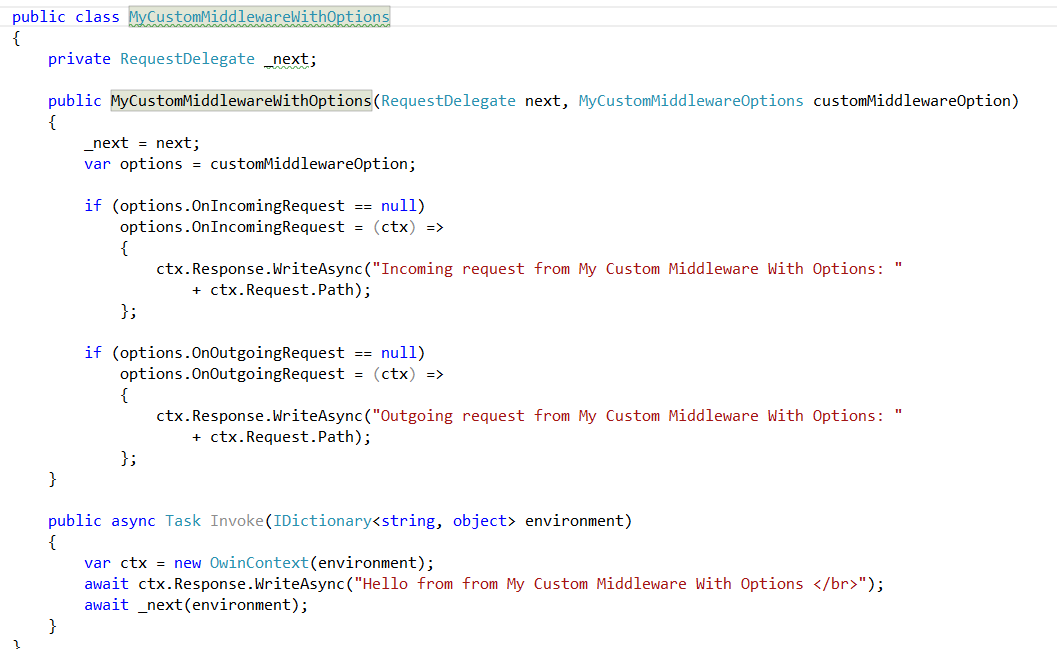
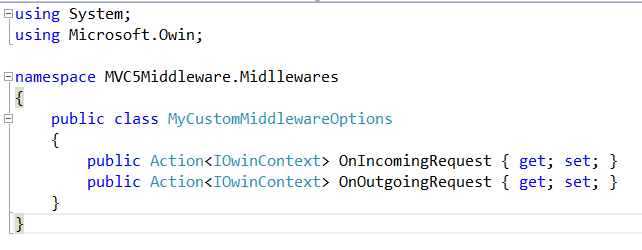
Creating a Custom Middleware with Options
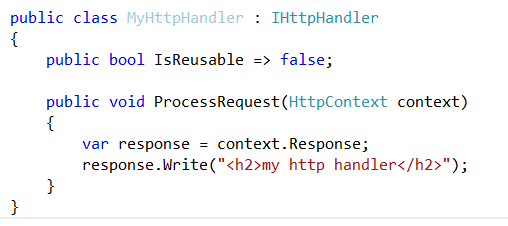
Creating a HttpHandler
An ASP.NET HTTP handler ==>
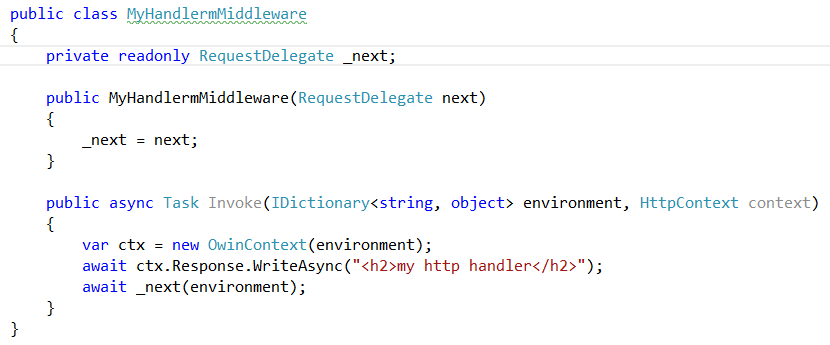
An ASP.NET HTTP handler using owin middleware ==>
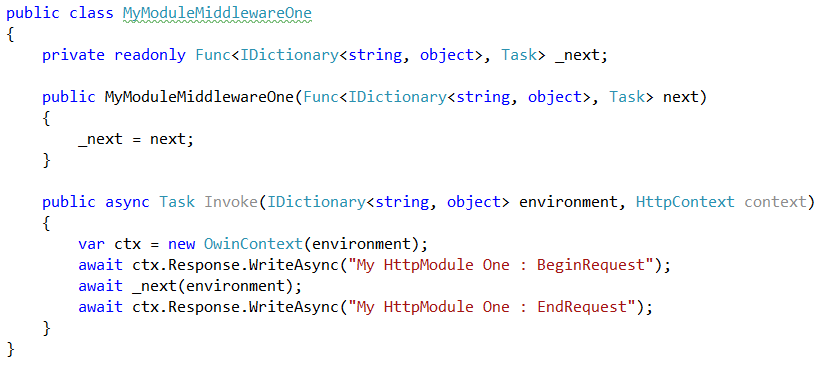
Creating a HttpModule
An ASP.NET HTTP module ==>

An ASP.NET HTTP Module using owin middleware ==>
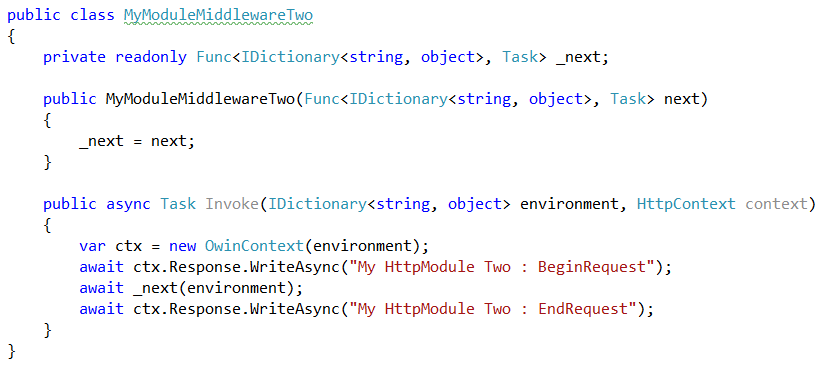
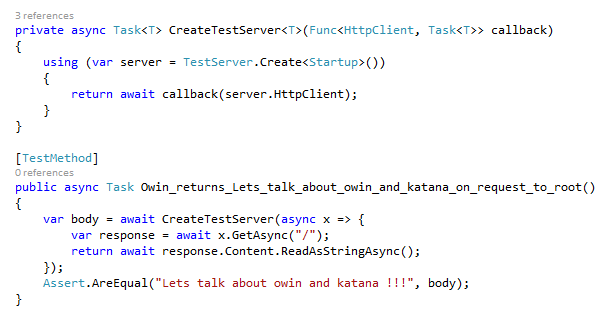
Unit Testing
using Microsoft.Owin.Testing;
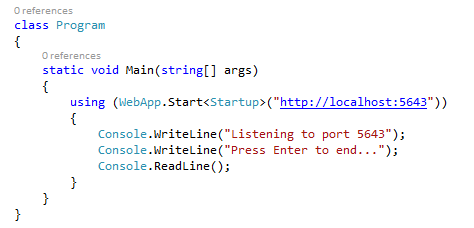
Self Hosting
using Microsoft.Owin.Hosting;
Thank you for reading.
Best regards
Highlighted on Articles Of The Day at 01/02/2017 (https://www.asp.net/community/articles)